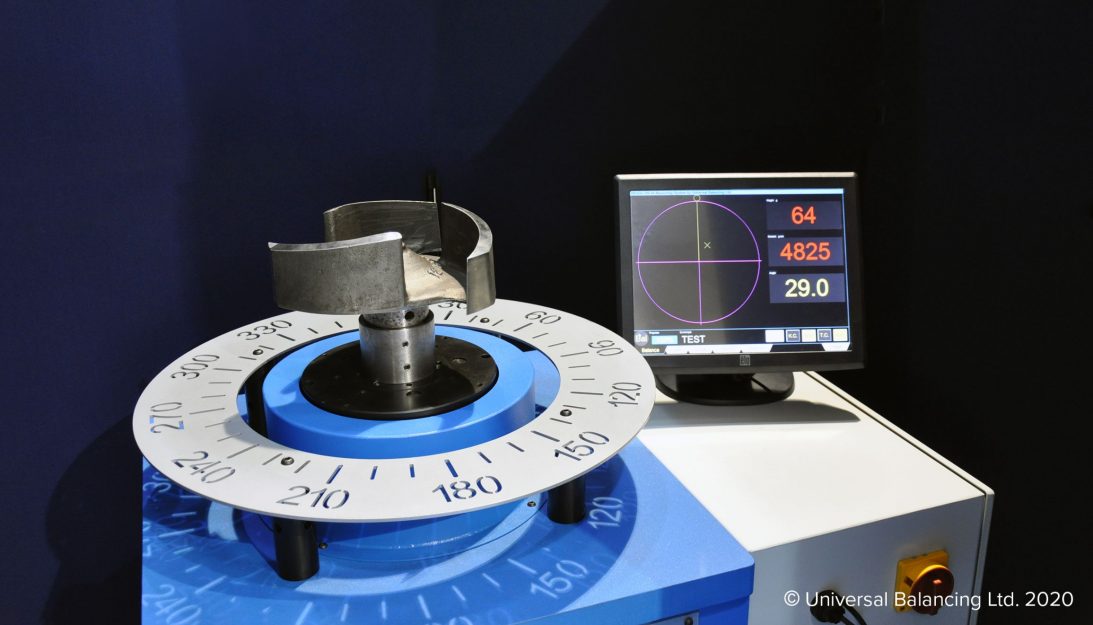
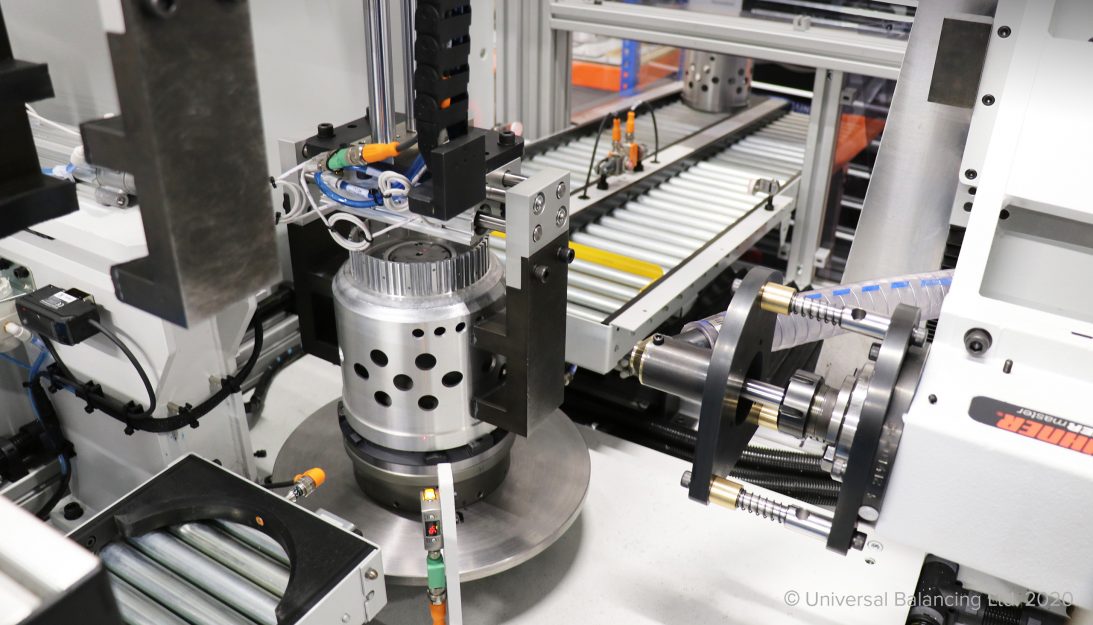
Propulsion
Power your module assembly line with Burke Porter assembly, balance and test automation
From traditional internal combustion engines to cutting-edge electric and hybrid technologies, we can help you achieve better power transfer quality and reduce Noise Vibration and Harshness.
Speak with an ExpertWhy Burke Porter Propulsion solutions?
Fast. Smooth. Quiet. Pick three for your vehicles with Burke Porter to ensure long-term performance on the road, satisfy customer expectations and reduce warranty returns associated with noise and vibration from powertrain components.
Burke Porter specializes in delivering cutting-edge assembly, balancing, and test solutions for propulsion systems including engines, axles, and e-mobility systems. Our extensive expertise and track record in providing customizable solutions tailored to your exact specifications ensure maximum efficiency and top-tier performance. Committed to safety, quality, and reliability, we consistently deliver projects on time and within budget, offering our clients the peace of mind they need for successful programs.

Flexible to your needs
No customer is the same. No site is the same. That’s why we offer each location and plant engineer customized solutions to meet your demanding specifications. Our specialists will ensure the entire process of procurement, design, assembly, and test is provided as a turnkey system. We take full responsibility from inquiry, quotation, supply, installation, and support.
Decades of durability
Like you, we develop high-performance technologies that are built to last. Backed by the industry’s deepest experience and practical know-how, Burke Porter delivers best-in-class products and services that reliably perform for decades. And, once they’re up and running, we continue to support those installations through the entire lifecycle of a program – from conception to eventual advancement.


Seamlessly integrated
Our propulsion assembly, balance, and test systems deliver another significant advantage: they seamlessly integrate with our end-of-line testing systems to enhance the overall quality, efficiency, and consistency of your environment. With Burke Porter, you get one partner for all of your automated module assembly and testing needs, simplifying the purchasing and project management process along with a single stop for service and support while giving you the confidence that everything runs as it should, 24/7.
Propulsion Products
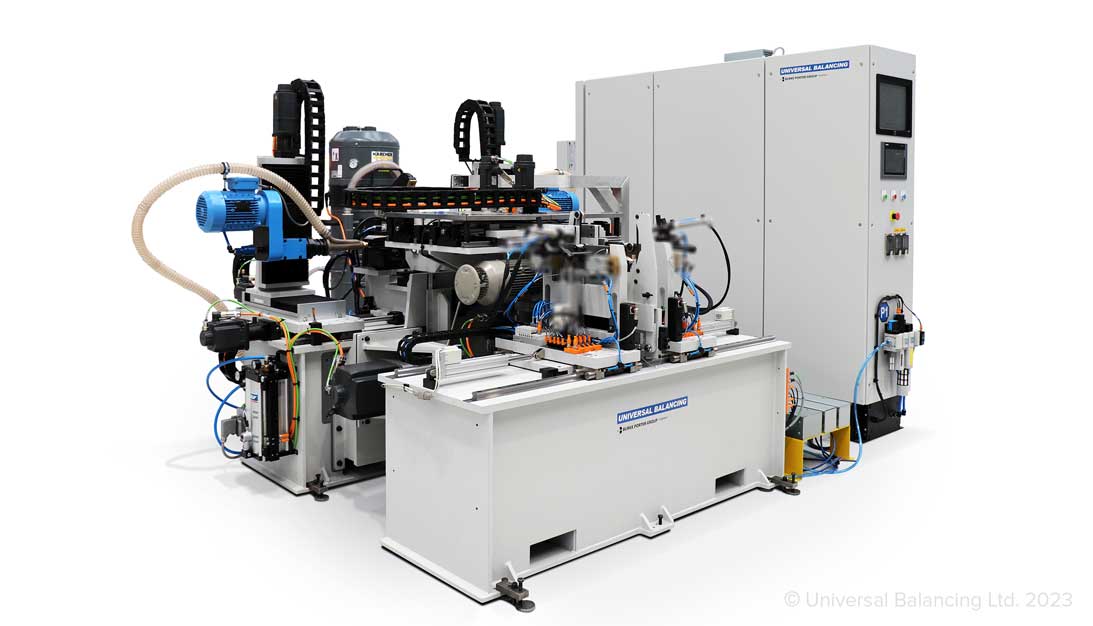
Balancing
Aircraft Wheel, Aircraft Tire and Aircraft Brake Balancers
Very easy to setup and operate Quick and accurate measurement Small footprint Low maintenance Short lead time
Learn moreBalancing
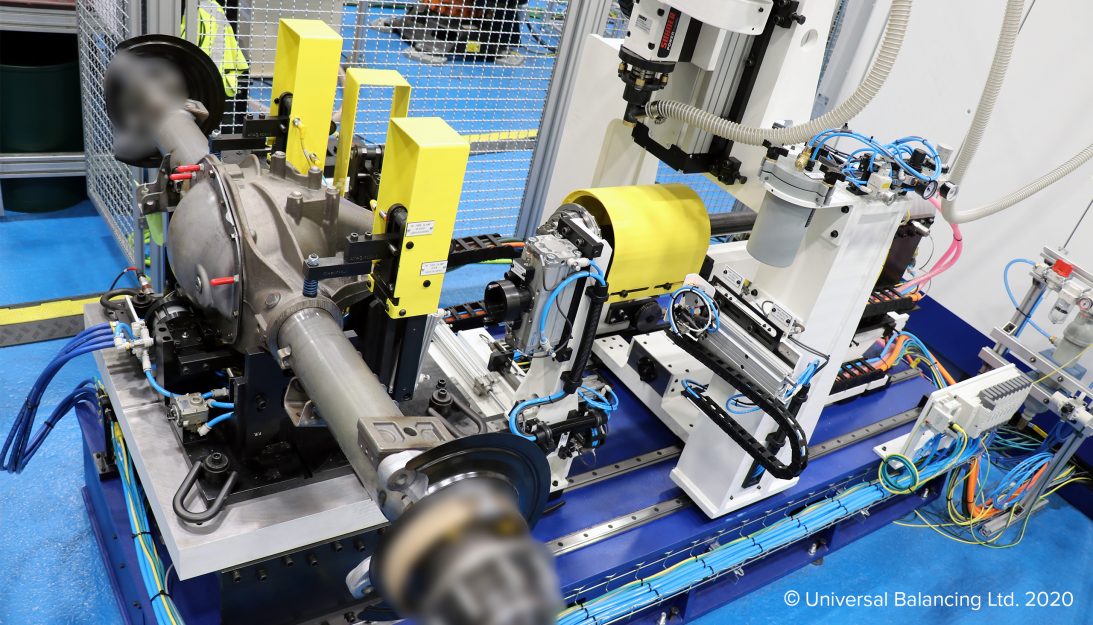
Axle Balancing Machines
Universal Balancing repeatedly produce innovative axle balancing machines that achieve the highest levels of accuracy and repeatability, and have even reduced the number of machines required when compared to alternative vendors. Working closely with customers to develop machines to balance any configuration of axle, Universal Balancing continuously enhance their technology to meet the latest and future production demands.
Learn moreBalancing
Software
Balancing Measuring System & Software
The capability of any balancer is the result of its balance measurement system, and Universal Balancing offers the most advanced available in the UNI-64 Windows based measuring system and the Windows-based Winbal balancing software.
Learn moreBalancing
Brake Rotor Balancing machines
Balancing machines for brake rotors, brake discs, brake hubs and brake drums. Automatic single or multi-station brake rotor balancing machine designed for high volume production lines. Intelligent in-process feedback optimizes production throughput and reduces rejects. Ultra-high accuracy. Repeatability of <5% part tolerance. Industry leading cycle time.
Learn moreBalancing
Clutch Balancers
Balancing machines for clutch components Automatic single or multi-station balancing machines designed for high volume production lines. Intelligent in-process feedback optimizes production throughput and reduces rejects. Ultra-high accuracy and repeatability of <10% part tolerance. Industry leading cycle time.
Learn moreTest
Clutch Testing
Our clutch burnishing and characterizing stations are able to test transfer cases and axles and burnish the clutch to remove the outer surface, stabilizing the part.
Learn moreBalancing
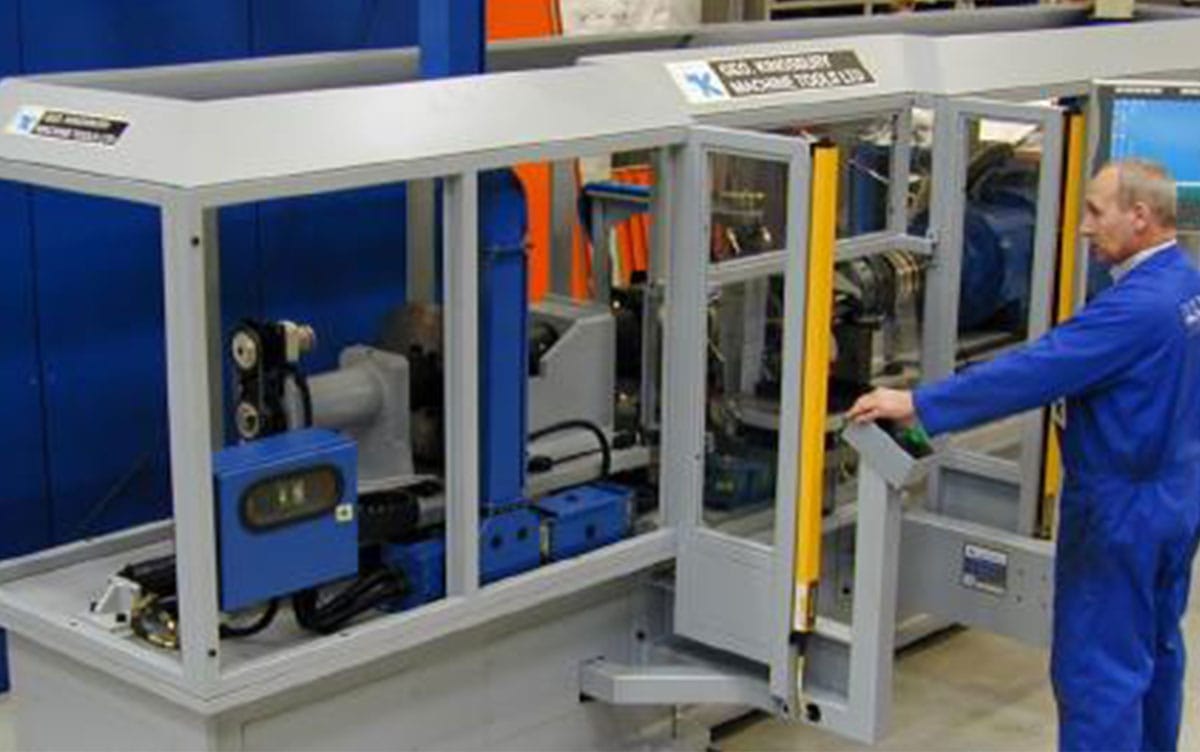
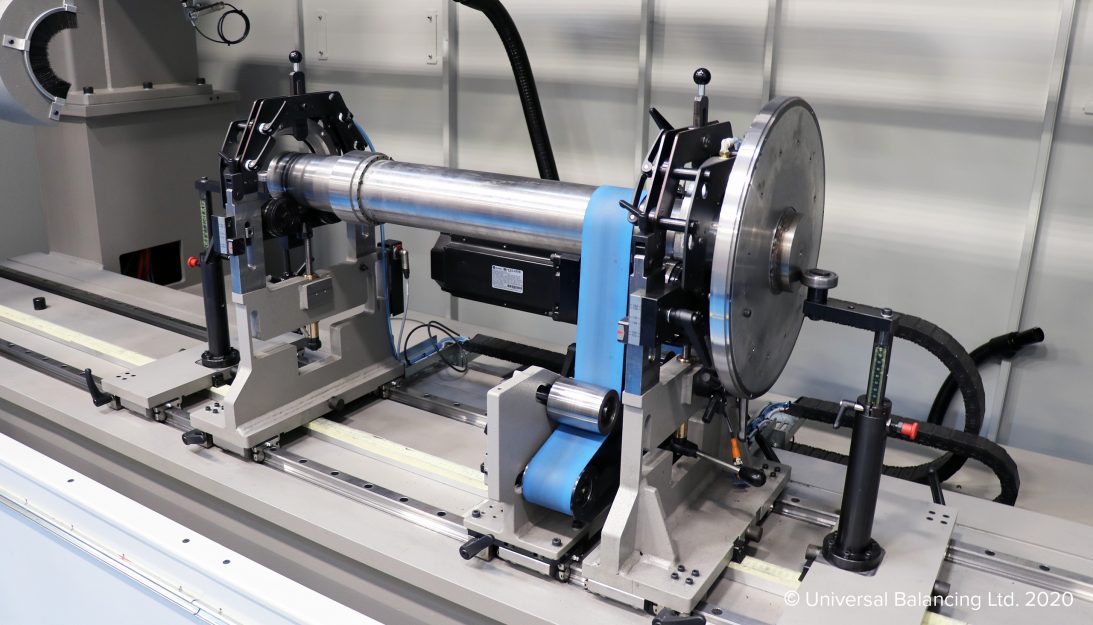
Crankshaft Balancing Machines
Automatic crankshaft balancing machines for light and heavy duty OEM’s and tier 1’s.
Automatic drilling and automatic loading
Manual and semi-auto crankshaft balancing machines for all industries
24/7 remote support and global support network
Learn moreBalancing
Driveshaft balancing machines
Universal Balancing has had a strong focus making driveshaft balancing machines since 1998. Working closely with customers to develop machines to balance any configuration of driveshaft, Universal Balancing continuously enhance their technology to meet the latest and future production demands.
Learn moreBalancing
Dynamic Balancing Machines
Dynamic balancing machines for all industries and rotor types. Manual and automatic dynamic balancing machine solutions for varying production demands. Integrated unbalance correction through drilling, milling, welding etc. 24/7 remote support and global support network
Learn moreBalancing
eRotor Balancing Machine
Automatic and manual electric motor rotor balancing. Configurations to suit any production volume. Accelerate, Measure & Decelerate as quick as 8 seconds. Error proof automatic changeover as standard. Ultra-high accuracy and repeatability of <10% part tolerance. Industry leading cycle time. Industry leading measuring system.
Learn moreBalancing
Fan Balancing Machines
Complete range of balancing machines for every type of fan and blower Simple to use software with intuitive unbalance correction displays Ultra-high accuracy and repeatability. Global supply and global support.
Learn moreBalancing
Flywheel Balancing Machines
Balancing machines for flywheels and flexplates. Automatic single or multi-station balancing machines designed for high volume production lines. Intelligent in-process feedback optimizes production throughput and reduces rejects. Ultra-high accuracy and repeatability of <10% part tolerance. Industry leading cycle time.
Learn moreBalancing
Horizontal Balancing machines
Horizontal balancing machines for any rotor type Balance parts from a few grams to 20,000 kg in one or two planes Special balancing machine designs for smaller and larger rotors Automatic and manual balancing machines for varying production demands 24/7 remote support and global support network
Learn moreBalancing
Propeller Balancers
Range of machines for all types of plane and boat propellers. Super simple to setup and operate. Low maintenance, high reliability. Global supply and global support.
Learn moreBalancing
Pump Balancing Machine
Balancing machines for all types of pump impellers and multi-stage assemblies. Custom pump balancing machine solutions for varying production demands. Optional automatic unbalance correction through drilling, milling, welding etc. Easy to setup and easier to use. 24/7 remote support and local service & support network
Learn moreBalancing
Rotor Balancing Machines
Rotors come in lots of different shapes and sizes. Find specific rotor balancing on our applications page or contact us so we can review your requirements together and recommend the ideal balancing machine for you.
Learn moreBalancing
Static Balancers
Vertical non-rotating and rotating static balancers for disc type rotors. For parts weighing up to 1500kg that need balancing in a single plane. Audit only balancers or optional integration with automatic production lines including off-balancer correction. 24/7 remote support and global support network.
Learn moreBalancing
Transmission Component Balancing Machines
Balancing machines for transmission shafts, gears, hubs and plates. Automatic single or multi-station balancing machines designed for high volume production lines. Intelligent in-process feedback optimizes production throughput and reduces rejects. Ultra-high accuracy. Repeatability of <10% part tolerance. Industry leading cycle time.
Learn moreBalancing
Vertical Balancing Machines
Vertical balancing machines for disc type rotors Balance parts from a few grams to 1,500kgs in one or two planes Various integrated correction such as drills, mills and welders Automatic and manual balancing machines for varying production demands 24/7 remote support and global support network
Learn more